08.JS的4种异步实现方式
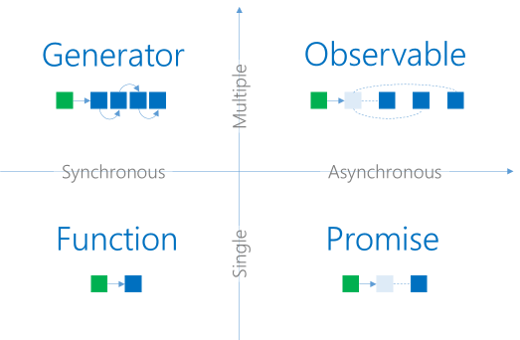
首先这4个都是异步返回处理完的结果,前3个是ES6异步按顺序处理并返回结果的官方语法范式,后一个是一个响应式编程库,前3个本质上可以看成是一个,不过是写法不一样而已,功能很简单,要么解决(成功)要么拒绝(失败),如果解决了一个那就可以往下再处理下一个,直到处理完成,如果拒绝处理则抛出异常并停止一步处理。而Observable则具备promise的特性的同时还更加强大些,如果promise返回的结果只能一个地方能有且只返回一次,而Observable可以多处订阅且可以返回多次数据的变动类型redux的状态更改订阅多次有效果,还有如配合管道结果进行处理如过滤地图等,而处理前也可以进行处理如防抖等,如果处理失败而异常也可以进行处理并再次发起重试。总之Observable可以对数据的处理前和处理后以及失败进行干预,这些是Promise没有的。
如果按回调的方式来处理顺序,且不是异步的,会这样写
function fun1(callback, funcParams) {
// 进行处理
console.log(`this is fun1 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
// 判断是否处理成功,是则下一步,否则返回结果
const isSucess = arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ? true : false;
return isSucess ? callback() : {funcName: 'fun1', reselt: 'error'}
}
function fun2(callback, funcParams) {
// 进行处理
console.log(`this is fun2 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
// 判断是否处理成功,是则下一步,否则返回结果
const isSucess = arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ? true : false;
return isSucess ? callback() : {funcName: 'fun2', reselt: 'error'}
}
function fun3(funcParams) {
// 进行处理
console.log(`this is fun3 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
// 这是最后一步,返回处理结果
const isSucess = arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ? true : false;
return isSucess ? {funcName: 'fun3', reselt: 'success'} : {funcName: 'fun3', reselt: 'error'}
}
const result = fun1(() => {
return fun2(() => {
return fun3('params for fun3')
}, 'params for fun2')
}, 'params for fun1')
console.log(result) // {funcName: "fun1", reselt: "error"} 如果result如果是'success'则是成功
注: 这还不是异步的处理,如果里面有定时等异步则会更复杂(我是没想到了),很难做到又异步又能报告处理到那里了且嵌套看起来就头痛。如果是promise则会简单很多。
1 以上按promise可以这么写
function fun1(funcParams) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 还可以定时等非阻塞之类的
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`this is fun1 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
resolve() : reject({funcName: 'fun1', result: 'error'})
}, 2000)
})
}
function fun2(funcParams) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 还可以定时等非阻塞之类的
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`this is fun2 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
resolve() : reject({funcName: 'fun2', result: 'error'})
}, 2000)
})
}
function fun3(funcParams) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 还可以定时等非阻塞之类的
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`this is fun2 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
resolve() : reject({funcName: 'fun2', result: 'error'})
}, 2000)
})
}
fun1('params for fun1')
.then(() => fun2('params for fun2'))
.then(() => fun3('params for fun3'))
.catch(e => console.log(e)) // 假如以上任意一步出错了,则会停止且在这里捕获异常
可以把promise理解为一条新建的流水线作业,在不影响浏览器主主线程的情况下,一个一个来处理then中的代码块。
2 以上promise按可以用asinc和await来调用
async function callAll() {
await fun1('param for fun1')
await fun2('param for fun2')
await fun3('param for fun3')
}
callAll().catch(e => {
console.log(e)
})
注: async标示该函数定义为prmise,await则标示调用的函数返回的是promise。
3 用Generator和yield来写则可以这样写
class demo {
generator;
constructor() {
// 在这里生成迭代器
this.generator = this.runAll();
this.generator.next();
}
fun1(funcParams) {
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`this is fun1 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
// 如果处理没有问题就下一步,否则则抛出异常
this.generator.next() : this.generator.throw(new Error('Something went rong in fun1'));
},1000)
}
fun2(funcParams) {
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`this is fun2 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
this.generator.next() : this.generator.throw(new Error('Something went rong in fun2'));
},1000)
}
fun3(funcParams) {
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(`this is fun3 and the params is ${funcParams}`)
const arr = ['success', 'error']
arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)] === 'success' ?
this.generator.next() : this.generator.throw(new Error('Something went rong in fun3'));
},1000)
}
*runAll()
{
try {
yield this.fun1('params for fun1')
yield this.fun2('params for fun2')
yield this.fun3('params for fun3')
}catch (e) {
console.log(e.message)
}
}
}
new demo();
// this is fun1 and the params is params for fun1
// VM1769:44 Something went rong in fun1
*注: 上面的写法还少了一步若是成功则返回各个步骤的处理结果,由于是在setTimeout写的,要返回结果当下也只有返回Promise 合适些。
注: 参考资料